Imagine a society in which all currency is digital, yet it is still issued by the government. That is precisely the goal of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs). Because they are backed by the government, CBDCs are more stable and secure than cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
The Evolution of Money and Digital Payments
To understand CBDCs, we need to look at how money itself has evolved.
Money has come a long way:
- Barter System – Trading goods and services directly.
- Gold & Silver Coins – Standardized value but cumbersome to carry.
- Paper Money & Banknotes – A more convenient form of currency.
- Digital Banking & Cards – The shift towards electronic transactions.
Rise of Digital Payments
The past two decades have seen a surge in:
- Online banking & digital wallets (PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay).
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin – Decentralized, but volatile.
- Blockchain technology – A secure and transparent way to record transactions.
As digital payments become more common, CBDCs offer a regulated substitute that combines the advantages of online banking with government regulation.
What Are CBDCs? – Definition & Key Characteristics
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) are digital representations of a nation’s fiat currency that is issued and controlled by the central bank. CBDCs are centralized, which means the government backs and regulates them, in contrast to cryptocurrencies.
Why Are CBDCs Important?
Governments and central banks worldwide are exploring CBDCs to:
- Modernize payment systems for the digital age.
- Promote financial inclusion, especially in underbanked regions.
- Provide a safer and more stable alternative to private cryptocurrencies.
CBDCs in 2025: A Growing Trend
As a crypto trend in 2025, more than 130 nations—representing an astounding 98% of the world’s GDP—are investigating or putting CBDCs into practice. Rapid digital transformation has the potential to change how we think about and utilize money, thanks to CBDCs.
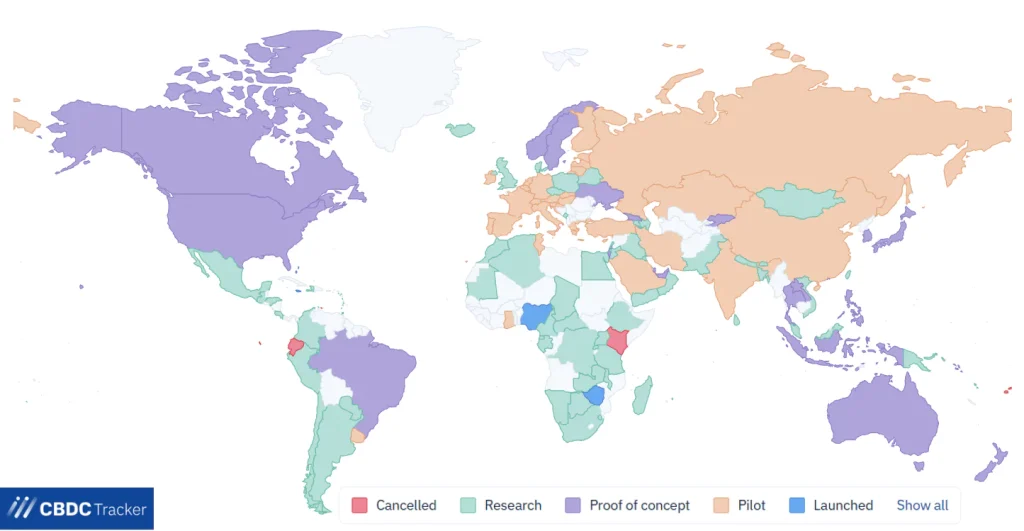
Key Characteristics of CBDCs
- Legal Tender – Recognized as an official form of payment.
- Centralized Control – Managed by the central bank.
- Stable Value – Pegged to the national currency, unlike volatile cryptocurrencies.
- Regulatory Framework – Operates under government regulations.
Types of CBDCs
- Retail CBDCs – Used by individuals and businesses for everyday transactions.
- Wholesale CBDCs – Used for interbank settlements and large-scale financial transactions.
Motivations Behind CBDC Development
Governments and central banks have multiple reasons for launching CBDCs:
1. Financial Inclusion
- Helps unbanked populations access digital payments.
- Provides a government-backed alternative to costly remittance services.
2. Payment Efficiency
- Lowers transaction costs and speeds up payments.
- Reduces dependence on intermediaries like banks and payment processors.
3. Monetary Policy Control
- Enables central banks to track money flows in real-time.
- Allows for programmable money, setting rules for spending and taxation.
4. Competition with Cryptocurrencies
- Offers a government-backed alternative to decentralized cryptocurrencies.
- Reduces reliance on volatile digital assets like Bitcoin.
How CBDCs Work
Central Bank Digital Currencies leverage advanced financial technologies, including:
- Blockchain & Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) – Ensures security, transparency, and immutability.
- Direct Accounts with Central Banks – Reducing reliance on commercial banks.
How Transactions Work
- Users hold CBDCs in a digital wallet, either via banks or directly with the central bank.
- Payments are processed instantly, without intermediaries.
- Transactions are secure and traceable, reducing fraud and tax evasion.
Integration with Traditional Banking
CBDCs are intended to enhance current financial systems, not to replace them. It is easy for users to transfer conventional fiat currency into CBDCs.
Benefits of CBDCs
1. Financial Inclusion
- Provides access to secure digital payments for the unbanked.
- Reduces dependence on cash, which can be costly to manage.
2. Faster & Cheaper Transactions
- Lowers cross-border payment fees.
- Reduces processing time for financial transactions.
3. Enhanced Monetary Policy
- Enables real-time tracking of money flows.
- Helps governments respond more effectively to economic crises.
4. Security & Transparency
- Reduces fraud and money laundering.
- Improves financial oversight and regulatory compliance.
Challenges and Risks
While CBDCs offer many benefits, they also come with challenges:
1. Privacy Concerns
- Governments could monitor transactions, raising surveillance fears.
- Balancing transparency with personal financial privacy is a key issue.
2. Cybersecurity Threats
- Digital currencies are vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks.
- Requires robust security measures to protect users.
3. Infrastructure Limitations
- Requires widespread internet access and digital literacy.
- Developing countries may struggle with implementation.
4. Impact on Traditional Banking
- Could reduce commercial bank deposits.
- May change how banks operate, affecting lending and interest rates.
Global Case Studies
Countries worldwide have already started experimenting with CBDCs.
China – Digital Yuan
- One of the most advanced CBDC projects.
- Over 7 trillion yuan in transactions by 2024.
Nigeria – eNaira
- Focused on financial inclusion for rural populations.
- Introduced a speed wallet app for easier adoption.
Bahamas – Sand Dollar
- Designed for remote island communities.
- Emphasizes simplicity and accessibility.
Sweden – e-Krona
- Aims to reduce reliance on cash.
- Focuses on privacy and regulatory frameworks.
Future of Central Bank Digital Currencies
1. Global Standards & Collaboration
- Organizations like the IMF and BIS are developing guidelines for cross-border CBDC use.
2. Integration with Emerging Technologies
- AI and blockchain will enhance CBDC security and efficiency.
3. Expansion of Use Cases
- Beyond payments, CBDCs could support loans, savings accounts, and trade finance.
4. Hybrid Financial Ecosystem
- CBDCs will likely coexist with cryptocurrencies and traditional fiat currencies.
Conclusion | Central Bank Digital Currencies
CBDCs mark an important shift in the world of finance. Digital currencies are being adopted by governments to improve security, financial inclusion, and payment efficiency. But there are still issues like cybersecurity threats and privacy issues.
Keeping up to date is essential as CBDC adoption increases. The future of money is digital, so keep an eye on developments in the future.













