Navigating the cryptocurrency world can feel like riding a roller coaster, with prices soaring to new heights one moment and plummeting to unexpected lows the next. Beneath this seeming chaos, though, are observable patterns called crypto market cycles. Understanding these cycles is crucial for making wise investing decisions and optimizing returns. Let’s explore the intriguing realm of cryptocurrency market cycles and learn what influences these price fluctuations.
What Are Crypto Market Cycles?
The term “crypto market cycles” describes the periodic upswings and downswings that cryptocurrencies go through. Many variables, such as macroeconomic conditions, technical advancements, market mood, and regulatory changes, influence these cycles. Investors can improve their trading techniques and make better selections by identifying and comprehending these cycles.
Phases of Crypto Market Cycles
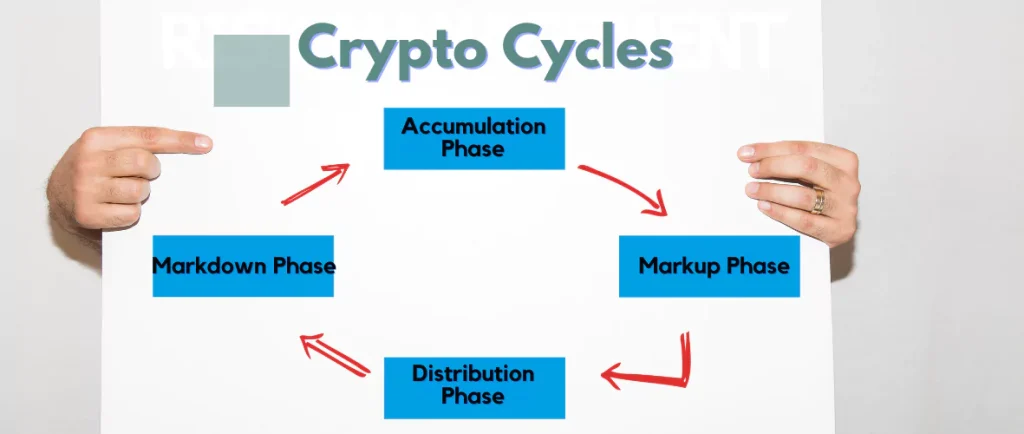
The four main stages of a cryptocurrency market cycle are usually distribution, markup, markdown, and accumulation. Investors can use the distinct traits and indicators of each phase to determine the direction of the market.
Accumulation Phase
The accumulation phase is the first stage of a market cycle. Prices are mostly stable at this stage, and investor sentiment is often negative. Many investors are hesitant to reenter the market during this period, which typically follows a significant market downturn.
The accumulation phase is characterized by low trade volumes, little price volatility, and a general lack of market interest. However, intelligent investors see this as an opportunity to buy assets at a lower cost. For example, Bitcoin was in an accumulating period at the start of 2020, with values ranging between $6,000 and $8,000. Those who identified this stage and invested later saw big rewards.
Markup Phase
The markup phase, which is characterized by rising prices and increased investor optimism, follows the accumulation period. This stage is typically spurred by positive news, technological advancements, or an increase in the use of cryptocurrency.
During the markup period, trading volumes increase dramatically, and prices climb greatly. The 2017 increase in the price of Bitcoin is an excellent example of this period. Bitcoin’s price rose from around $1,000 at the start of the year to around $20,000 by December, thanks to increased public interest and media coverage.
Distribution Phase
The distribution phase corresponds to the top of the market cycle. Prices have reached their greatest point, and market sentiment is overwhelmingly bullish. However, this phase also indicates that the market is becoming saturated, and a fall is likely.
The distribution phase is characterized by huge trading volumes, considerable price volatility, and an infusion of new, inexperienced investors into the market. During Bitcoin’s peak in December 2017, the cryptocurrency market was in its distribution stage. Many investors, motivated by FOMO (fear of missing out), rushed to buy at the high, only to see prices fall shortly thereafter.
Markdown Phase
The markdown phase of the market cycle is characterized by falling prices and rising investor pessimism. This phase occurs after the distribution phase and could last for a long time.
During the markdown period, trading volumes drop and prices fall significantly. The fall of the Bitcoin market in 2018 is an excellent example of this era. Bitcoin’s price fell from approximately $20,000 in December 2017 to around $3,000 in December 2018, causing huge losses for many investors.
Factors Influencing Crypto Market Cycles
Several variables drive cryptocurrency market cycles, including market sentiment, macroeconomic conditions, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Understanding these characteristics can help investors better predict and respond to market fluctuations.
Market Sentiment
Investor psychology and emotions significantly impact market cycles. Market attitude can swing from great optimism to intense dread, amplifying price fluctuations. For example, encouraging news about regulatory acceptance or technology improvements might boost investor confidence and cause prices to rise. Conversely, negative news, such as security breaches or regulatory crackdowns, can cause panic selling and price drops.
Macroeconomic Factors
Global economic conditions also influence crypto market cycles. Interest rates, inflation, and economic growth all have an impact on investor behavior and market patterns. For example, during the COVID-19 outbreak, many investors flocked to cryptocurrency as a hedge against economic instability, which pushed prices upward. The effect of macroeconomic factors on cryptocurrency markets demonstrates the interdependence of global financial institutions.
Technological Developments
Innovations and technological advancements can have a significant impact on market cycles. The introduction of new technology or enhancements to existing ones may pique investors’ attention and drive implementation. For example, the publication of Ethereum 2.0, which promises greater scalability and security, aroused significant attention and shifted market trends. Technological breakthroughs frequently serve as catalysts for market movements, stressing the importance of staying current with industry trends.
Regulatory Environment
Government laws and regulations may have a substantial impact on cryptocurrency markets. Positive regulatory developments, such as the legalization of cryptocurrencies or the establishment of advantageous tax legislation, can boost investor confidence and drive market growth. Restrictive laws, such as prohibitions on cryptocurrency trading and mining, can dampen market sentiment and induce price decreases. One notable example is China’s cryptocurrency ban, which generated enormous market volatility and disrupted the global mining business.
Identifying Market Cycle Phases
Recognizing the different phases of market cycles is essential for investors looking to make informed decisions. Both technical and fundamental analyses play a crucial role in identifying these phases.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis uses historical price data and trade volumes to find patterns and trends. Investors can use a variety of techniques and indicators to identify the different stages of a market cycle. Some popular technical analysis tools include:
- Moving Averages: Moving averages help smooth out price data, making it easier to identify trends. For example, the 200-day moving average is often used to identify long-term trends. When the price is above the moving average, it suggests an uptrend, while a price below the moving average indicates a downtrend.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements. It ranges from 0 to 100, with values above 70 indicating overbought conditions and values below 30 indicating oversold conditions. RSI can help identify potential turning points in the market cycle.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): The MACD is a trend-following indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a cryptocurrency’s price. It consists of the MACD line, the signal line, and the histogram. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it indicates a bullish trend, while a cross below suggests a bearish trend.
Fundamental Analysis
Assessing a cryptocurrency’s inherent value using criteria including its technology, use case, team, and market demand is known as fundamental analysis. Investors can determine the stages of a market cycle and make better decisions on a cryptocurrency’s development potential by evaluating its underlying worth.
Tutorials on conducting fundamental analysis can be invaluable for investors. Some key aspects to consider include:
- Project Team: Assess the experience and expertise of the project’s team members. A strong team with a proven track record can significantly increase the likelihood of a project’s success.
- Use Case and Technology: Evaluate the cryptocurrency’s use case and the technology behind it. A unique and valuable use case, combined with innovative technology, can drive adoption and long-term growth.
- Market Demand: Analyze the market demand for the cryptocurrency. High demand and growing adoption can indicate strong potential for future growth.
Conclusion | Crypto Market Cycles
The ebb and flow of the cryptocurrency industry is referred to as a crypto market cycle, and it influences price fluctuations and investor sentiment. Investors can better navigate the crypto market’s unpredictable environment by understanding these cycles and making well-informed decisions that reduce risks while capitalizing on opportunities.













